Short for miniature circuit breaker. Not main circuit breaker. Each sub circuit in the consumer unit starts with a MCB. Protects against overcurrent.
Advantages
Section titled “Advantages”Advantages of a MCB over fuses:
- Non-destructive
- Fast
- Shorter tripping times under moderate overcurrents
- Immediate indication of faulty current
- Manual operation: can be used as a circuit control switch
- Easy to use
- No stock of fuses required
- Reclosing can be effected at once after the fault has been cleared
- More accurate
MCBs are more expensive than fuses.
Ratings
Section titled “Ratings”- Rated current
- Rated voltage (single phase and 3-phase)
Mechanism
Section titled “Mechanism”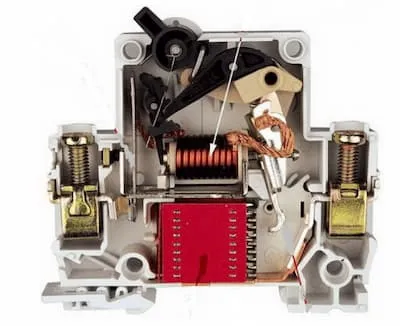
Has 4 functional components:
- A thermal overload trip (bi-metal)
For small overloads and time-graded operation - An electromagnetic short-circuit trip
For high fault currents and near-instantaneous operation - A switching mechanism with contacts
- Arc exhausting system
Function of the thermal device
Section titled “Function of the thermal device”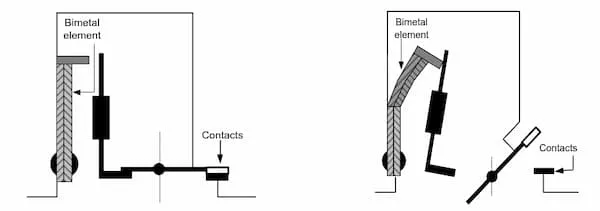
Consists of a bi-metal strip. When overheated from overload current, the bi-metal strip is deflected. The deflection depends on the heat which depends on:
- Intensity of current flow
- Duration
Function of the EM device
Section titled “Function of the EM device”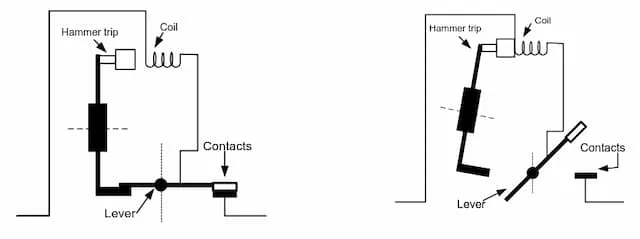
Consists of a solenoid coil. Load current is set to flow through the coil.
In this coil, there is a fixed iron-core with a movable armature. When the current exceeds the rated value, the coil exerts sufficient electromagnetic force to attract the armature against the force of the spring. A switch mechanism is activated by the lever, to open the contacts.