Impedance & Admittance
Impedance (Z)
Here:
: Resistance : Reactance
Admittance (Y)
Inverse of impedance.
Here:
: Conductance : Susceptance
From the definitions:
For simple circuit elements
Resistor
Let
No changes in frequency, phase angle.
Inductor
Let
Reactance of the inductor is
Capacitor
Let
Reactance of the capacitor (capacitive reactance) is
For complex circuit elements
Real Inductor
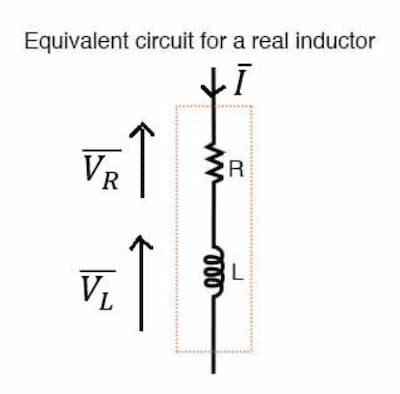
Take
From here
RLC series circuit
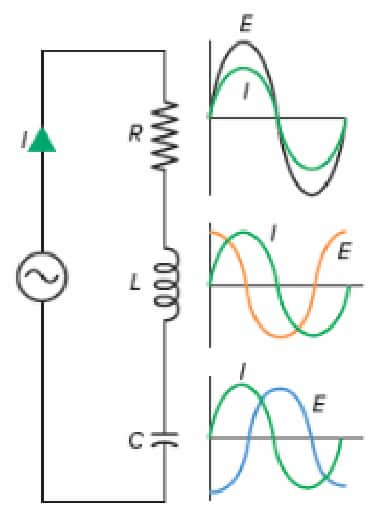
Complex impedances are added up to find the total impedance of a series circuit.
For a series circuit
Total impedance is the sum of each component’s impedance.
For a parallel circuit
Total admittance is the sum of each component’s admittance.