Another type of relative equilibrium. If a fluid-contained vessel is rotating at a constant angular velocity, the fluid will reach a relative equilibrium position and rotate with the vessel. Under this condition, the fluid is said to be in Forced Vortex Motion.
Here:
- - angular velocity
Equation of the free surface
Section titled “Equation of the free surface”On the free surface .
The free surface is parabolic. The constant part can be found by a known point of the free surface. For ease of calculations, the axes can be chosen so that the free surface passes through . In that case, .
Vertical Pressure Distribution
Section titled “Vertical Pressure Distribution”Pressure increases linearly with height. Increases exponentially with radial distance. Isobars are parabolic.
Volume of the fluid
Section titled “Volume of the fluid”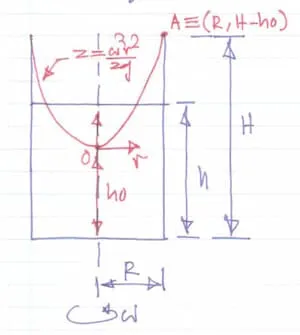
Total volume of the fluid is: