Acts normal to the surface on the centre of pressure with a magnitude of:
Thrust=submerged area×Pc
C is the centroid of the submerged area. Pc is the pressure at the
centroid.
yp=yc+A⋅ycIcc
Here:
- A - Total submerged area
- yp - Distance to centre of pressure measured along the submerged surface
from the free surface
- yc - Distance to C measured along the submerged surface from the free
surface
- Icc - Second moment of submerged area about the centroidal axis
parallel to the free surface
| Shape | Description | yp |
|---|
| Parallelogram | Base b. Height h. Base is at the free surface. | 32h |
| Triangle | Base b. Height h. Base is at the free surface. | 65h |
| Circle | Radius r. Center is at a depth r. | 45r |
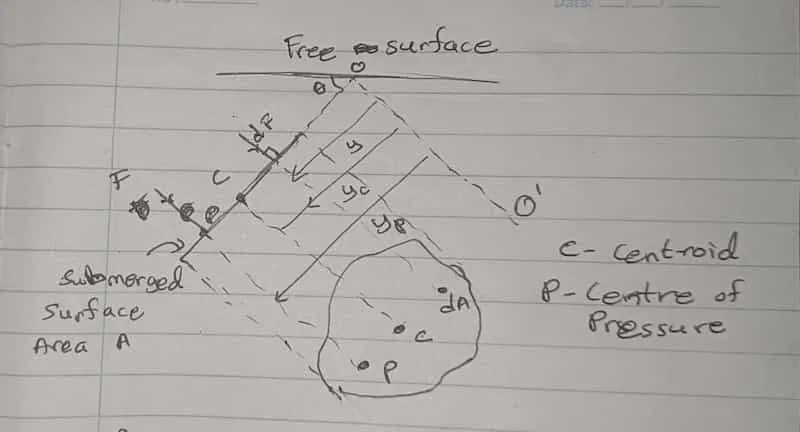
All forces acting on the surface is normal to the surface. Therefore F is
normal to the surface.
F=∫AdF=∫ApdA=∫AysinθρgdA
F=sinθρg∫AydA=sinθρg⋅Ayc=A⋅ycsinθρg
F=APc
F⋅yp=∫AydF
yp=∫AdF∫AydF=∫AysinθρgdA∫Ay(ysinθρg)dA=∫AydA∫Ay2dA
yp=AycIoo=yc+AycIcc
Fx=Thrust exerted on the vertical projection of the submerged surface
Fy=Weight of the fluid above submerged surface
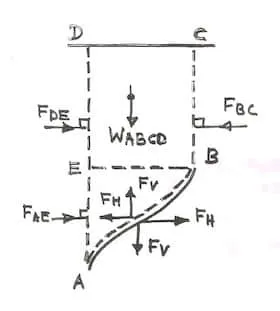
For the equilibrium of the fluid volume ABCDA.
Fy=WABCDA
For the equilibrium of the fluid volume ABEA.
Fx=FAE

