Revise Vectors unit from G.C.E (A/L) Combined Mathematics.
Suppose p=ai+bj+ck. Direction
cosines of p are cosα,cosβ,cosγ where
α,β,γ are the angles p makes with x,y,z axes.
Unit vector in the direction of
p=icosα+jcosβ+kcosγ.
Because of this:
cos2α+cos2β+cos2γ=1
Ratio of the direction cosines is called as direction ratio.
cosα:cosβ:cosγ
a×b=∣a∣∣b∣sin(θ)n=iaxbxjaybykazbz
n is the unit normal vector to a and b. Direction is based on
the right hand rule.
a×b=0⟹∣a∣=0∨∣b∣=0∨a∥b
Cross products between i, j, k are circular.
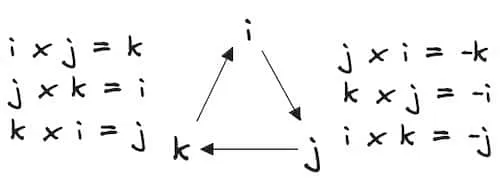
- a×a=0
- (a×b)=−(b×a)
- a×(b+c)=(a×b)+(a×c)
- Area of a parallelogram ABCD=∣AB×AD∣
[a,b,c]=a⋅(b×c)=axbxcxaybycyazbzcz
- [a,b,c]=a⋅(b×c)=(a×b)⋅c
- [a,b,c]=[b,c,a]=[c,a,b]=−[a,c,b]
- Swapping any 2 vectors will negate the product.
- [a,b,c]=0 iff a, b, c are coplanar.
- Volume of a parallelepiped with a, b, c as adjacent edges = [a,b,c]
- Volume of a tetrahedron with a, b, c as adjacent edges = 61[a,b,c]
a×(b×c)=(a⋅c)b−(a⋅b)c
Resulting vector lies in the plane that contains b and c.
