Rigid body
Section titled “Rigid body”A solid body that doesn’t deform.
Degrees of freedom
Section titled “Degrees of freedom”In the motion of a rigid body in 2D kinematics, there are degrees of freedom.
- Movement along direction
- Movement along direction
- Rotation about direction
In 3D, there are degrees of freedom: movement and rotation along each direction.
Translation
Section titled “Translation”Movement that changes the position of an object. Translation can be done through a rectilinear or curvilinear path. Axes of the body always stays parallel.
Rotation
Section titled “Rotation”Circular movement of an object about a fixed axis that is perpendicular to the plane.
General 2D motion
Section titled “General 2D motion”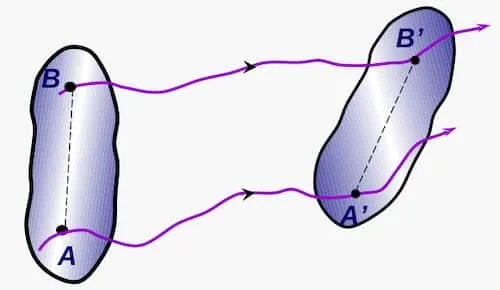
Mixture of translation and rotation.
Here:
- - Angular velocity of relative to
- - Velocity of relative to
- - Acceleration of relative to
- - Position vector of relative to . It’s constant.
In general motion, each particle of the body has a different velocity at every instance.
Instantaneous centre of rotation
Section titled “Instantaneous centre of rotation”The point that has velocity at a particular instant of time. This point might be changing throughout the motion. Denoted by .
It can be imagined that the object is momentarily having a pure rotation about this centre .
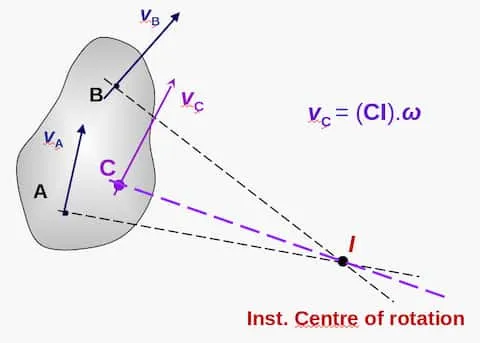
can be found by drawing a line perpendicular at the velocity vectors at 2 different points and finding their intersection point.
Centrode
Section titled “Centrode”The locus of instantaneous centres during the motion.