A branch of mechanics, which deals with motion of bodies.
2 parts:
- Kinematics: the study of geometric aspects of motion (not referencing the forces)
- Kinetics: the analysis of the forces that cause the motion
Kinematics of a particle
Section titled “Kinematics of a particle”A particle has a mass and negligible size.
Rectilinear motion
Section titled “Rectilinear motion”When the motion of a particle is along a straight line.
Suppose is the distance to the particle from a fixed point on its motion path.
- is its instantaneous velocity.
- is its instantaneous acceleration.
Curvilinear motion
Section titled “Curvilinear motion”When the motion of a particle is along a curve.
Suppose is the position vector of the particle.
- Instantaneous velocity
- Instantaneous speed
- Instantaneous acceleration
2D motion of a particle
Section titled “2D motion of a particle”Rectangular form
Section titled “Rectangular form”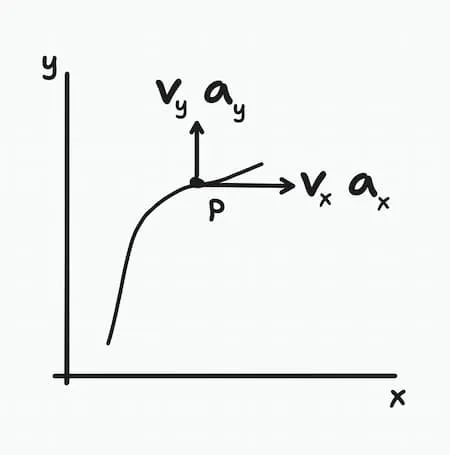
Polar form
Section titled “Polar form”
Velocity have a transverse and radial components.
- Transverse component
- Radial component
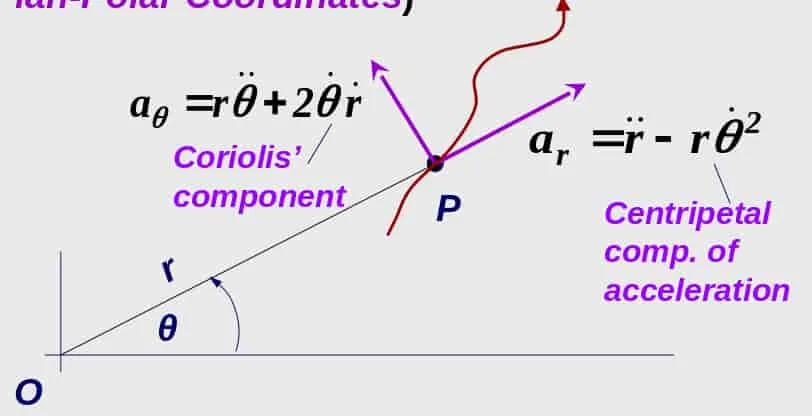
Acceleration also have a transverse and radial components.
- Transverse component
- In vector equation:
- Radial component
In the acceleration:
- Coriolis’ component of acceleration:
- Centripetal component of acceleration:
Effects of Coriolis’ component
Section titled “Effects of Coriolis’ component”- Objects reflect to the right in the northern hemisphere
- Objects reflect to the left in the southern hemisphere
- Maximum deflections occur at the poles. No deflection at the equator.
Unit vectors
Section titled “Unit vectors”Unit vectors in transverse and radial directions are denoted by and respectively.