CPU in today’s computers are microprocessors. A CPU:
- performs logical & arithmetic operations
- controls all the other components and subsystems
Components of a CPU
Section titled “Components of a CPU”Arithmetic & Logical Unit
Section titled “Arithmetic & Logical Unit”Arithmetic unit handles arithmetic operations. Logical unit handles logical operations.
Control Unit
Section titled “Control Unit”Controls the operation of the CPU and rest of the machine. Handles the decoding of instructions.
Registers
Section titled “Registers”A type of memory that can hold a unit of data. Can be used for both data processing and control functionalities.
Type of registers
Section titled “Type of registers”Program Counter
Section titled “Program Counter”Keeps track of memory address of the next instruction to be executed. Directly connected to ALU.
Instruction Register
Section titled “Instruction Register”After an instruction is fetched into the CPU, it is stored in IR for execution. Keeping IR closer to CU (in the scale of micrometers) enables faster execution speed.
Accumulator
Section titled “Accumulator”Where result of arithmetic or logical operation is stored immediately.
Flag Register
Section titled “Flag Register”Stores the status of the last operation carried out by ALU.
General Purpose Registers
Section titled “General Purpose Registers”Can be used to various tasks. Used to store immediate results of the ALU. Number of GPRs vary with the CPU. Usually denoted as “B”, “C” and so on.
Internal Structure
Section titled “Internal Structure”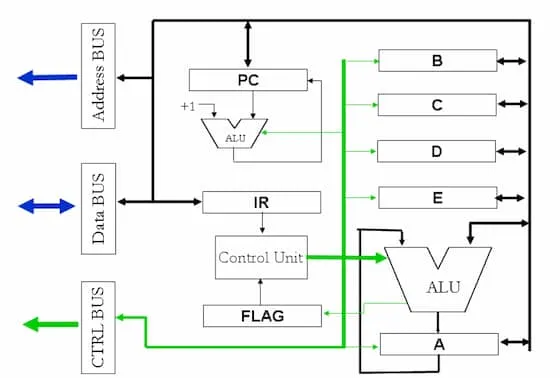
- There is a secondary ALU after PC. That increments the PC after fetching a new instruction.
- ALU accepts maximum 2 inputs. One input should come from accumulator.
Enhancing CPU Performance
Section titled “Enhancing CPU Performance”Instruction pre-fetching
Section titled “Instruction pre-fetching”The process of fetching next instruction while current instruction is still executing. Reduces idle time of CPU.
Instruction pipelining
Section titled “Instruction pipelining”The process of dividing instruction execution cycle into multiple stages. Those multiple stages will be executed in parallel. Increases thoroughput of the microprocessor.
Hyper Threading
Section titled “Hyper Threading”Allows different resources of the CPU to be used at the same time. CPU, BIOS, OS, and chipset have to support HT technology to use this.
Multicore processors
Section titled “Multicore processors”2 or more separate microprocessors, combined onto a single Silicon chip. Higher performance gain compared to HT.