Non-volatile or permanent. High capacity. Low cost-per-megabyte.
Can be categorized into 3 types:
Optical
Section titled “Optical”Uses tiny visible light beams or laser.
Examples:
- Compact Disk - Read Only Memory
- Compact Disk - Recordable
- Compact Disk - ReWritable
- Digital Video Disk
- Digital Video Disk - Recordable
- Digital Video Disk - ReWritable
Compact Disk
Section titled “Compact Disk”Made of polycarbonate wafer, 120mm in diameter and 1.2mm thick, with a 15mm hole in the centre.
The wafer base is stamped or moulded with a single physical track in a spiral configuration starting from the inside of the disk and spiralling outwards. When examined under a microscope, pits (raised bumps along the track) and lands (flat areas between the pits) can be seen. Pits are 0 and lands are 1.
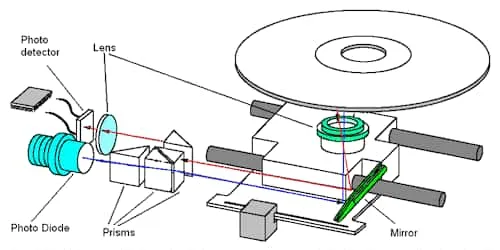
These components are used in CD technology.
- Photodiode - to generate the light beam
- Servomotor - to position the beam onto the correct track
- Phototransistor - to convert light into electrical impulses
Flash storage
Section titled “Flash storage”Built using EEPROMs. High capacity and high transfer speed compared to other forms of portable media. Low latency, low noise, low power consumption, high reliability.
SSDs use flash memory technology. RAM modules are also starting to use flash memory technology.
Categorized into 2, based on operational characteristics:
- NAND Flash
- NOR Flash
Flash memory stores information in an array of memory cells made from floating gate transistors. In the traditional flash drives, each cell stores a single bit of data. However, newer flash devices known as multi-level cell devices can store more than one bit per cell by choosing between multiple levels of electrical charge.