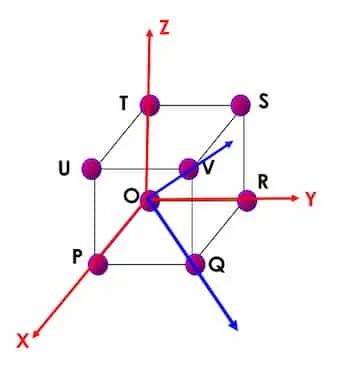
Any vertex can be chosen as the origin.
Notation
Section titled “Notation”- Minus noted with a bar
- Addition and subtraction is carried out like vectors
- - Atom/Vertex
- - Direction, no commas
- - Family of directions
- - Plane, no commas
- - Family of planes
- Always will be whole numbers. Fractions must be multiplied by LCM.
Direction
Section titled “Direction”Equivalent directions are grouped into a family.
Direction families
Section titled “Direction families”- No of planes:
- No of planes:
- No of planes:
The above are the common directions. There are other directions as well.
Show the direction
Section titled “Show the direction”To show the direction , for example:
Take the point . Divide by the highest number (, in this case) to bring the point inside the unit cell. The resulting point will be . The direction is given by vector from to the resulting point.
Close packed direction
Section titled “Close packed direction”All neighbour atoms in a direction touch each other. For example: of fcc.
- If sitting on any axes, move the origin.
- Find the intercepts. if parallel.
- Find the reciprocals.
Plane families
Section titled “Plane families”- Denotes as
- No of planes:
- Denotes as
- No of planes:
- Denotes as
- No of planes:
The above are the common planes. There are other planes as well.
Show the plane
Section titled “Show the plane”- Divide by the smallest non-zero number.
- Find the reciprocals. means parallel to the axis.
Close packed plane
Section titled “Close packed plane”All neighbour atoms in a crystal plane touch each other. For example: of fcc.
Planar Density / Aerial Density
Section titled “Planar Density / Aerial Density”Number of atoms in a unit area in a specific plane. Differs between different planes in a single crystal structure.