A rolled up sheet of graphene.
Classifications
Section titled “Classifications”Based on structure
Section titled “Based on structure”- Single wall carbon nanotubes (SWNT)
- Multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWNT)
Similar to graphite but rolled up as a set of sheets.
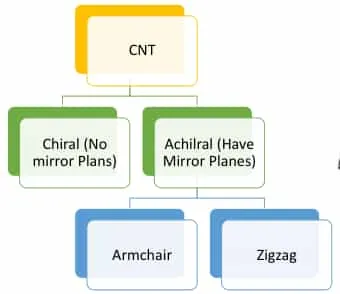
Based on Chirality
Section titled “Based on Chirality”Chirality means the way that graphene sheet is oriented with respect to the axis of carbon nanotube.
Achiral
Section titled “Achiral”Have mirror planes. Has 2 types.
- Armchair
- Zigzag
Armchair
Section titled “Armchair”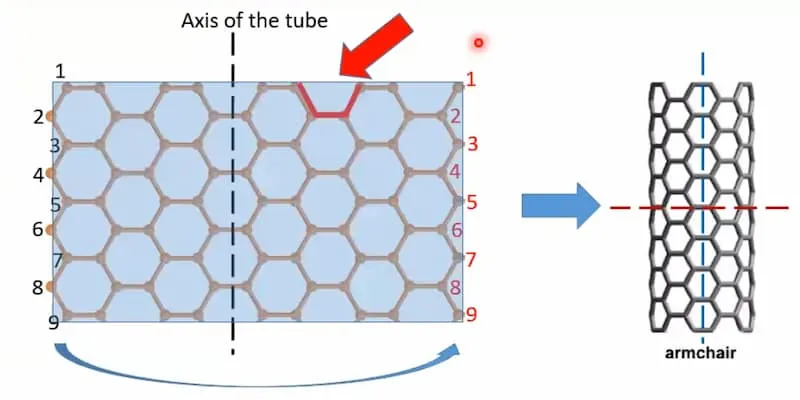
Circumference has a repeating armchair structure.
Zigzag
Section titled “Zigzag”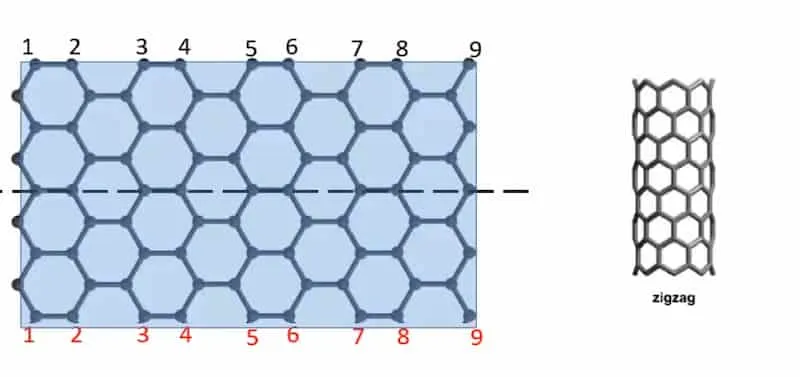
Circumference has a repeating zigzag structure.
Chiral
Section titled “Chiral”No mirror planes. Definition for the chiral type is later explained.
Definitions
Section titled “Definitions”Equivalent Atoms
Section titled “Equivalent Atoms”Equivalent atoms means the atoms having the same surrounding.
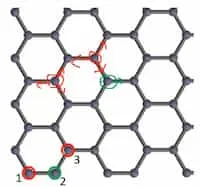
In graphene, next-near neighbours are equivalent atoms.
When a graphene sheet is rolled to create a CNT, only equivalent atoms can be connected.
Primitive Vectors
Section titled “Primitive Vectors”Vectors used to describe a unit cell.
For graphene, any 2 adjacent sides of the unit cell can be used as the primitive vectors.
Lattice Vectors
Section titled “Lattice Vectors”Any vector connecting 2 equivalent atoms. A lattice vector can be expressed in terms of primitive vectors.
Chiral Vector
Section titled “Chiral Vector”The vector that constructs the circumference of a CNT. Also called as Circumferential vector.
(n,m) notation
Section titled “(n,m) notation”If the chiral vector can be expressed as where are the primitive vectors, then the notation for the nanotube is
- : zigzag tube
- : armchair tube
- Otherwise: chiral tube
Chiral Angle
Section titled “Chiral Angle”Angle between the chiral vector and nearest zigzag angle.
For a tube where and :
- : armchair tube
- : zigzag tube
- : chiral tube
Chiral Vector Length
Section titled “Chiral Vector Length”For a tube, the chiral vector’s length is given by:
Here is the bond length of C-C.
Diameter of CNT
Section titled “Diameter of CNT”The diameter can be expressed by:
Properties
Section titled “Properties”- Mechanical properties
- High young’s modulus
Depends on tube diameter, multi-walled or single-walled but not tube chirality. Multi-walled CNTs have higher young’s modulus. - Sustains higher strain
- High young’s modulus
- Electrical properties
- Depends on chirality and size
- Exhibits superconductivity at
- Band structure changes with chirality
- Thermal properties
- Conducts thermal energy only in the axial direction; radial direction is insulating
Chirality-dependent
Section titled “Chirality-dependent”For a tube:
- If , its armchair typed and is metallic (good conductors)
- If is a integer multiple of : small band gap semiconductors
- Else: large band gap semiconductors
Band gap decreases as the radius increases.
Applications
Section titled “Applications”- Conductive or reinforced plastic
- CNT based transistors
- Molecular electronics
- Energy storage devices
- Biomedical applications