Most domestic installations in Sri Lanka use single phase. For higher loads, third phase can be installed on request. The electricity is supplied through a service cable which includes a live wire and a neutral wire and in .
The service cable first goes into the energy meter.
Electric meter
Section titled “Electric meter”Installed by the electric utility, for billing purposes. Can either be electromechanical, electronic, or smart meter. Measures energy in . Up to the electric meter, the equipment belongs to the supply utility. Consumer’s installation starts from the main switch. After the electric meter, the live and neutral wires are connected to the main switch in the consumer board.
Consumer unit
Section titled “Consumer unit”Aka. distribution unit. Size of the consumer unit depends on the size of the property and how many circuits are being controlled.
- Controls the distribution of power
- Provides protection against faults
Main circuit breaker
Section titled “Main circuit breaker”Aka. main switch. Controls the electricity to the rest of the consumer unit and all the circuits in the property. Can be operated manually to cut the power. Disconnects both live and neutral wires. Operates automatically if the overall load demand grows too high. Has a rated voltage and rated current.
After the main switch, the wires are connected to the RCCB. After RCCB:
- the live wire goes to live bus bar
- the neutral wire goes to neutral bus bar
- the earth bus bar will have a wire earthed separately
Bus bar
Section titled “Bus bar”A conductive metal thing. Used to reduce the number of wires. There are earth, live and neutral bus bars.
After the live bus bar, the live wire is connected to multiple MCBs.
Wiring a final circuit
Section titled “Wiring a final circuit”Loop-in method
Section titled “Loop-in method”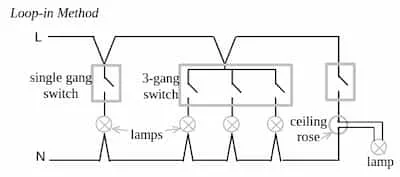
Enables all joints and terminations in a single final circuit to be made at ceiling roses, switches or other accessories. This makes all joints accessible for testing and alterations. Each final circuit has both its live and neutral conductors terminating at the consumer unit. Wires are usually laid in PVC conduits.
Two-way switches
Section titled “Two-way switches”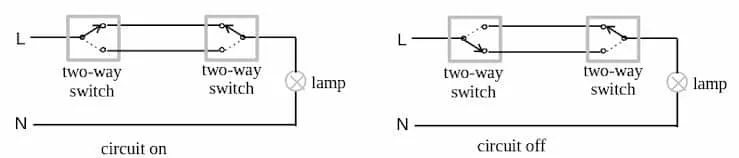
Used when it’s necessary to operate an equipment from 2 positions.
Socket outlets
Section titled “Socket outlets”There are 3 types of socket outlets.
- - Circular holes
- - Rectangular holes. Currently recommended one. Safest one compared to other. Better because of flat-to-flat contact.
- - Bigger circular holes
Final circuits for socket outlets
Section titled “Final circuits for socket outlets”Electrical equipments can be wired in 2 ways.
Radial circuit
Section titled “Radial circuit”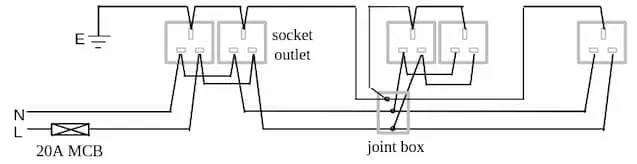
Each circuit commences from consumer unit through an MCB (or fuse), loops into each socket outlet and terminates at the last socket outlet.
To connect 2 equipments in radial connection:
- 2 switches are required. Both switches are connected to a MCB. Each connect to the equipments
- 2 live wire connects 2 switches to of them to a MCB
- Neutral wires of the 2 equipments is connected to the neutral bus bar.
Ring circuit
Section titled “Ring circuit”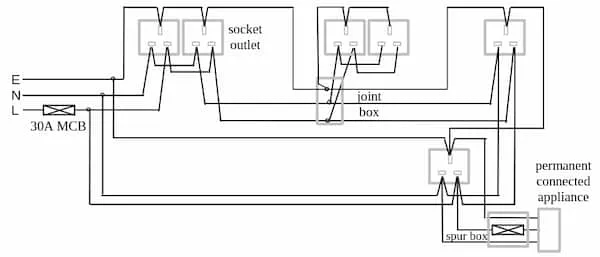
Each circuit commences from consumer unit through an MCB (or fuse), loops into each socket outlet and returns to the same MCB (or fuse) in the consumer unit.
Looping must be done for the live, neutral and the protective conductors in separate rings. Electricity can flow from either ends. This increases the current carrying capacity without increasing the wiring size.
A ring circuit can only be used when:
- The floor area served by the ring does not exceed
- Maximum demand of the circuit doesn’t exceed the MCB (or fuse) rating
To connect 2 equipments in ring connection:
- A live wire starts from a MCB, connects to the 2 equipments and come back to the MCB
- Similarily neutral wire is connected in a ring starting from neutral bus bar